Monetary conservatism: why the Central Bank maintains a tight policy despite business demands
The Central Bank has been steadily implementing a phased reduction of the rate — the third in 2025 after a cut from 21% to 20% in June and to 18% in July. As Elvira Nabiullina noted, persistent inflation expectations and an acceleration in corporate lending have prompted a cautious approach.
Particular attention is being paid to risks related to fiscal policy and the geopolitical situation.
Business demands for a more substantial rate cut are justified by a severe downturn in key sectors. Alexander Shevelev (Severstal) reports a 14–15% decline in metal consumption, comparing the situation to the crisis of the 1990s. The Ministry of Economic Development supports this position, pointing to "substantial room for easing," amic.ru reports.
Budget execution for January–August 2025 shows a deficit of 4.2 trillion rubles (1.9% of GDP), which exceeds planned annual figures. Nabiullina directly linked the prospects for further rate cuts to the dynamics of the budget deficit.
Sectoral consequences
Construction sector: minimal effect from the cut.
Credit market: lagging adjustment of rates on retail products.
Banking system: maintenance of differentiated deposit rates.
The rate is expected to reach 13–14% by the end of 2025, provided inflationary processes and budgetary parameters stabilize.
The Central Bank’s policy is aimed at shaping a savings-oriented behavioral model and long-term macroeconomic stability, although this limits the real sector’s recovery prospects in the short term.
The actions of the Bank of Russia reflect the classic dilemma faced by central banks in emerging economies: the choice between immediate growth stimulus and ensuring long-term stability.
Experts believe that the current course indicates a priority on inflation control, which is consistent with global practice in conditions of worldwide uncertainty.
Другие Новости Кирова (НЗК)
 Astrological forecast for the week: a time of order and new opportunities.
The horoscope for the week of September 29 to October 5 indicates the beginning of a period favorable for establishing useful connections, intellectual work, and putting documents and financial matters in order.
Astrological forecast for the week: a time of order and new opportunities.
The horoscope for the week of September 29 to October 5 indicates the beginning of a period favorable for establishing useful connections, intellectual work, and putting documents and financial matters in order.
 Four suspects in a waste fraud case have been remanded in custody.
Petrozavodsk City Court in Karelia has ordered that two senior figures involved in a high-profile criminal case on fraud in the field of waste management be remanded in custody. The former head of Avtospetstrans LLC, Evgeny Moshnikov, and the former Minister of Natural Resources of Karelia, Alexey Shchepin, will be held in custody until November 23.
Four suspects in a waste fraud case have been remanded in custody.
Petrozavodsk City Court in Karelia has ordered that two senior figures involved in a high-profile criminal case on fraud in the field of waste management be remanded in custody. The former head of Avtospetstrans LLC, Evgeny Moshnikov, and the former Minister of Natural Resources of Karelia, Alexey Shchepin, will be held in custody until November 23.
 The top-level educational program at VyatGU has been recognized as one of the best in the country.
Starting in the 2025/26 academic year, Vyatka State University, at the initiative of the Ministry of Digital Development of the Russian Federation and with the participation of the Analytical Center under the Government of the Russian Federation, is implementing a top-level educational program, "Software and Hardware Solutions for Artificial Intelligence Systems."
The top-level educational program at VyatGU has been recognized as one of the best in the country.
Starting in the 2025/26 academic year, Vyatka State University, at the initiative of the Ministry of Digital Development of the Russian Federation and with the participation of the Analytical Center under the Government of the Russian Federation, is implementing a top-level educational program, "Software and Hardware Solutions for Artificial Intelligence Systems."
 Sirens will wail in Kirov.
Russia's Ministry of Emergency Situations warned citizens about a check of the alert systems.
Sirens will wail in Kirov.
Russia's Ministry of Emergency Situations warned citizens about a check of the alert systems.
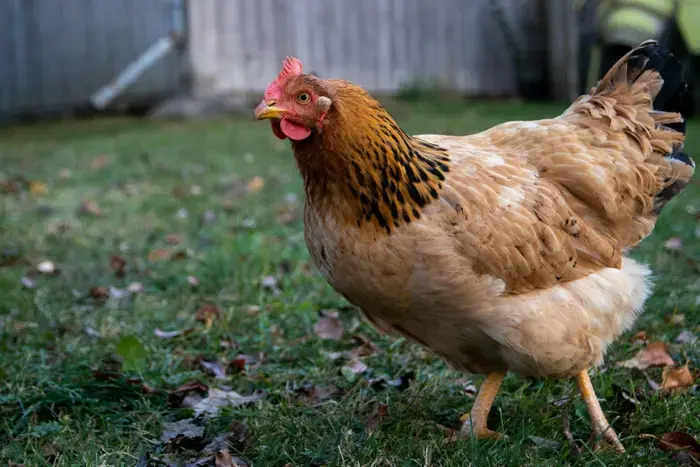 A Kirov resident raises chickens under a social contract.
A father of a large family took advantage of a social assistance program and was able to start a small chicken farm.
A Kirov resident raises chickens under a social contract.
A father of a large family took advantage of a social assistance program and was able to start a small chicken farm.
 In the Kirov region, they "made off with" 200,000 rubles.
The Prosecutor's Office of the Yuryansky District of Kirov Oblast identified violations in the protection and preservation of forests.
In the Kirov region, they "made off with" 200,000 rubles.
The Prosecutor's Office of the Yuryansky District of Kirov Oblast identified violations in the protection and preservation of forests.
Monetary conservatism: why the Central Bank maintains a tight policy despite business demands
The cut of the key rate to 17% on September 12 confirmed the Bank of Russia’s commitment to a conservative course, sparking a discussion about the balance between inflationary risks and the needs of the real sector. The regulator’s decision reflects a comprehensive approach to managing macroeconomic stability amid persistent uncertainty.
